HTTP
💡
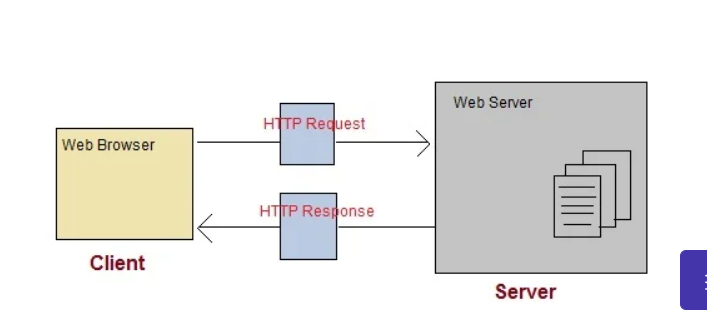
✈️HTTP
HyperText Transfer Protocol
- is the set of rules for transferring files — such as text, images, sound, video, and other multimedia files -- over the web.
- <request, response> pairs
- is a stateless protocol:
- after the response is delivered to the client → unconnect → the server no longer stores the request anymore.
- the store information of other side is the work of client, not server.
Read more:

 What is HTTP and how does it work? Hypertext Transfer Protocol DefinitionHTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is the fundamental protocol used for transferring files on the internet. This definition explains how HTTP the request and response process between client and server, as well as the differences between HTTP and HTTPS and common response status codes.
What is HTTP and how does it work? Hypertext Transfer Protocol DefinitionHTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is the fundamental protocol used for transferring files on the internet. This definition explains how HTTP the request and response process between client and server, as well as the differences between HTTP and HTTPS and common response status codes.https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/definition/HTTP-Hypertext-Transfer-Protocol

💡
Request Message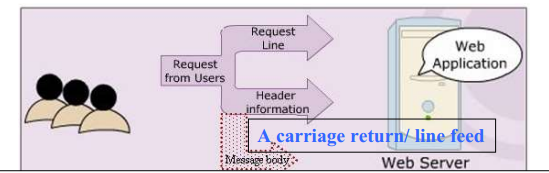
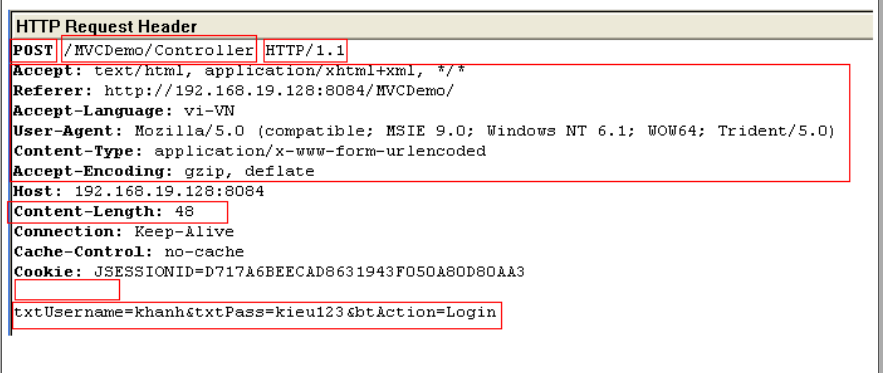
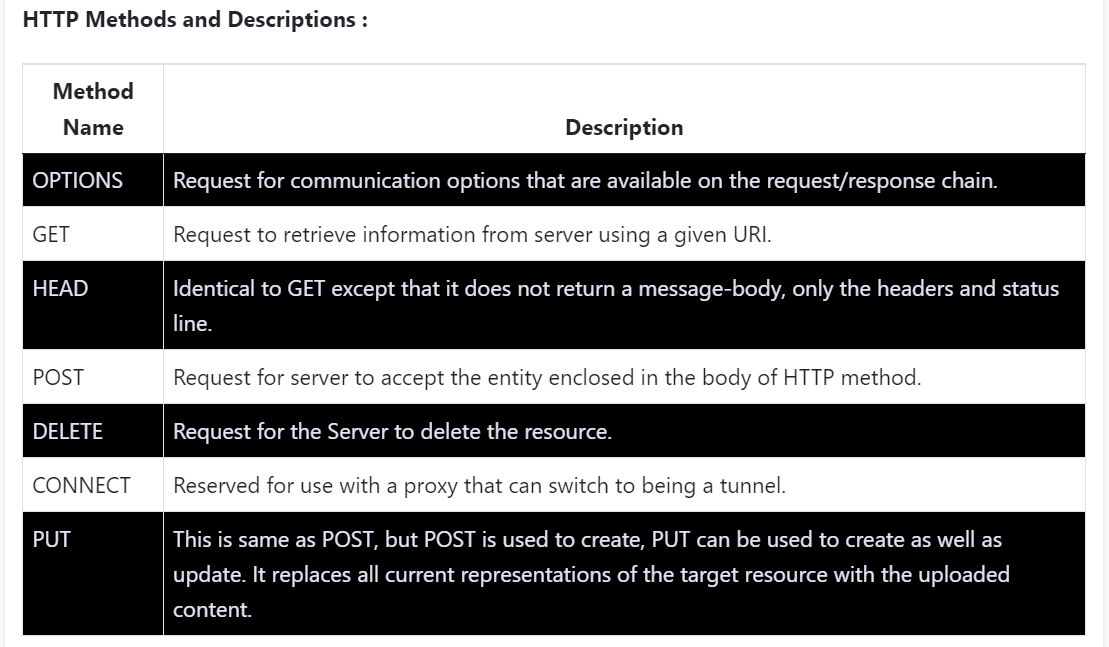
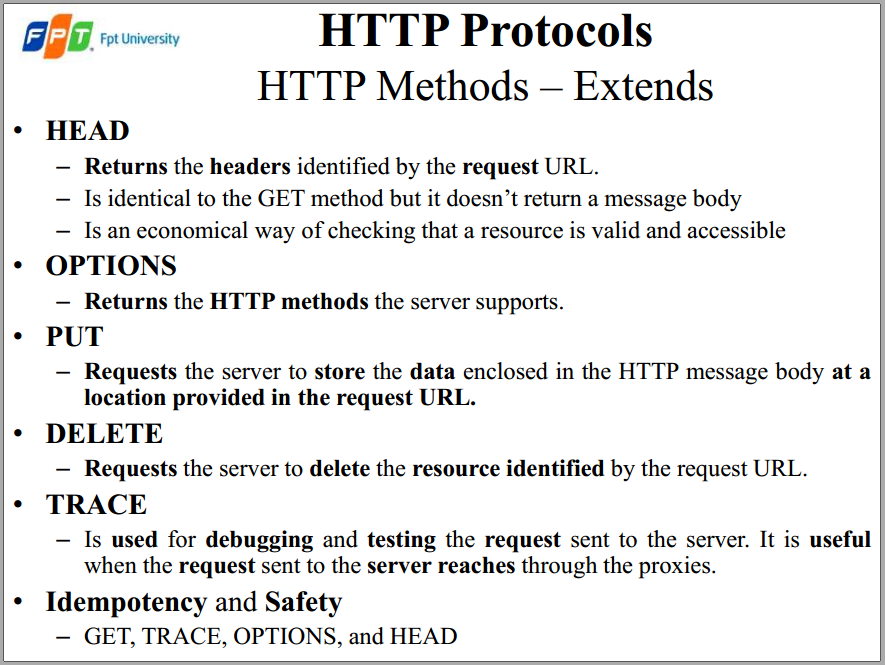
- Request line:
HTTP methodURIHTTP/1.1
Header information:
- name:value form provide information from the client like user-agent, accept (for media types), referer (URL that request target to), content-length,…
Message body: (optional)
- take an enter space/carriage return/line feed to separate with header
- pretty much anything (a set of parameters and values, an image file intending to upload)
- is optional depending on the method


💡
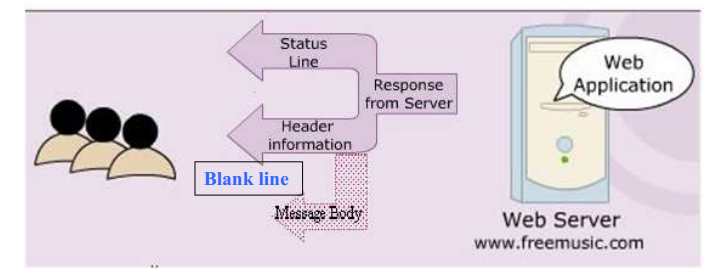
Response Message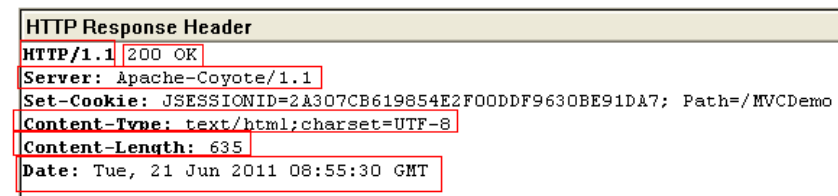
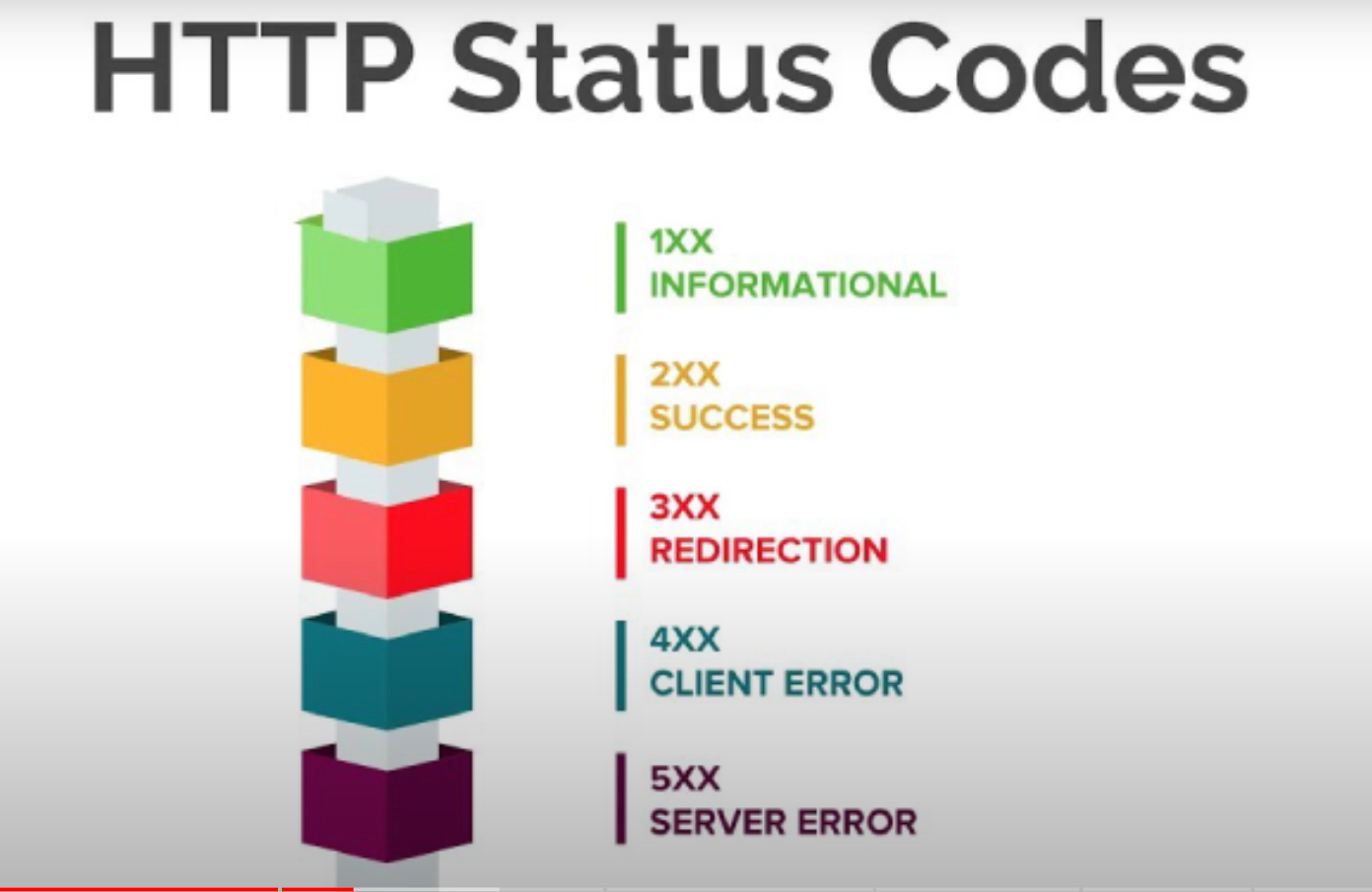
- Status line:
HTTP/1.1Response CodeStatus Massage
- Header Information:
- name:value form provide information from the server like
- server: JavaWebServer
- Last-modified: Tuesday, 24-Mar-09 8:30:34 GMT
- content-length: 100
- tính bằng bytes.
- cơ sở để dựa vào khi tiến hành/dừng đọc dữ liệu.
- content type: text/plain
- browser xác định type và lựa chọn cách hiển thị phù hợp.
- name:value form provide information from the server like

💡
💡