JDBC
💡
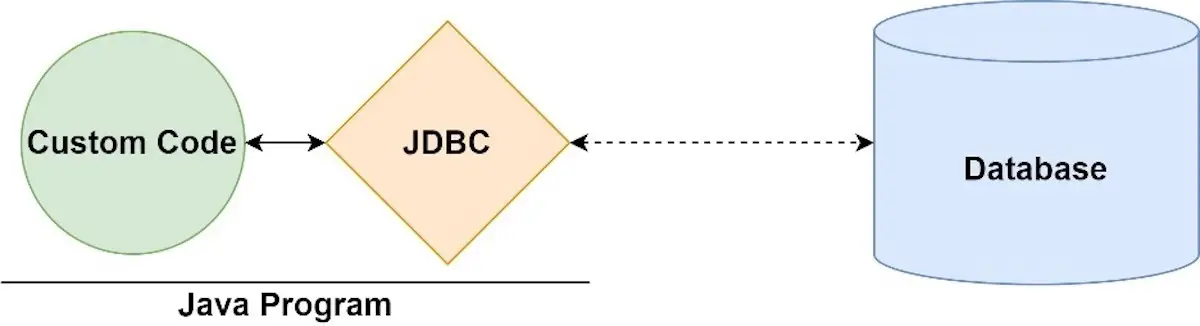
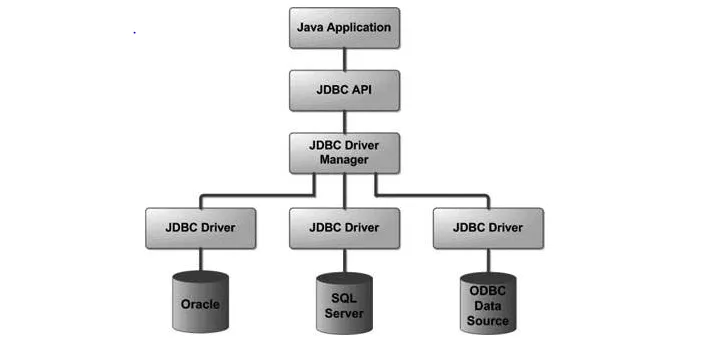
JDBC:🔑JDBC in action
- is an application programming interface (API) for the programming language Java.
- defines how the client can connect and interact with a Database.
💡
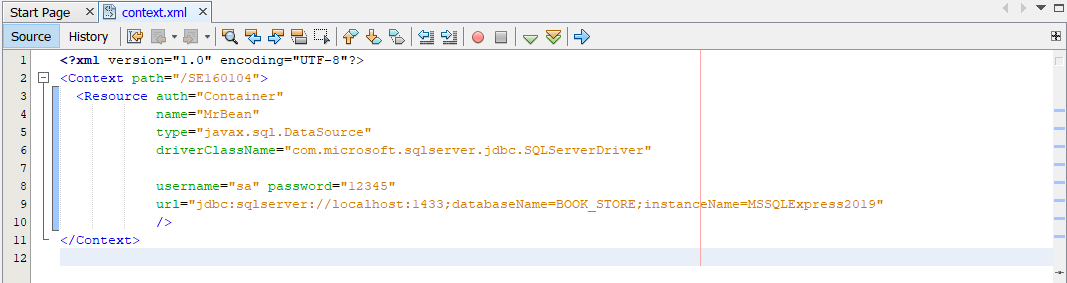
JDBC ’s parts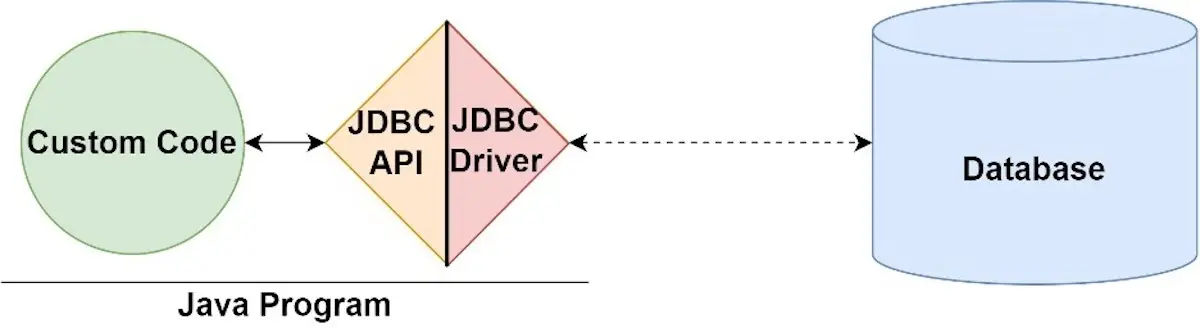

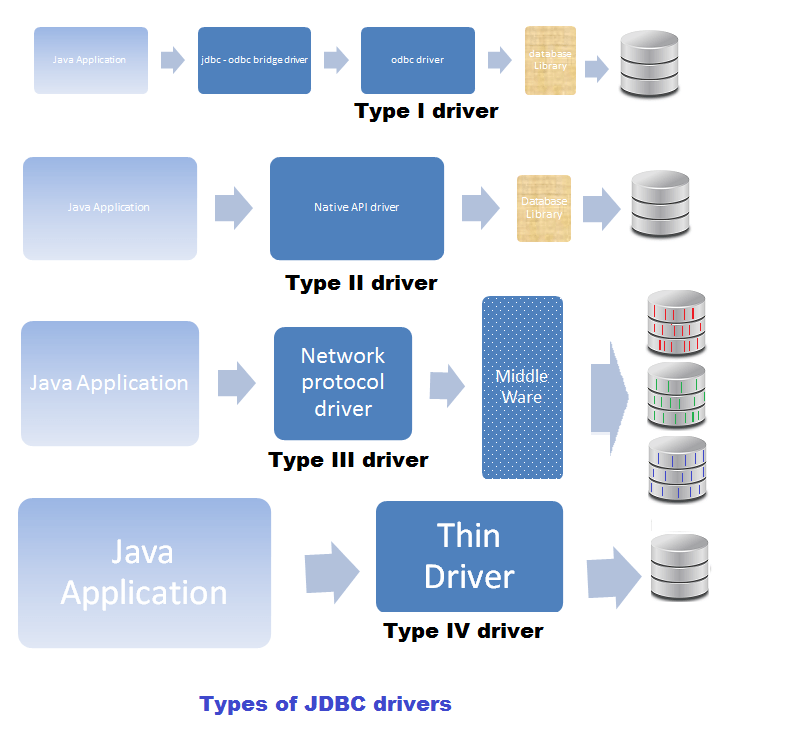
JDBC Driver
Driver:
- a software component
- convert JDBC calls —middle layers—> native calls on DB server.
- gives out the connection to the database
- implements the protocol for transferring the query and result between client and database.
- provided by a specific provider for a specific database.
DriverManager:
- an interface between users and drivers.
- maintains a list of drivers created for different databases
- handles establishing a connection between a database and the appropriate driver.
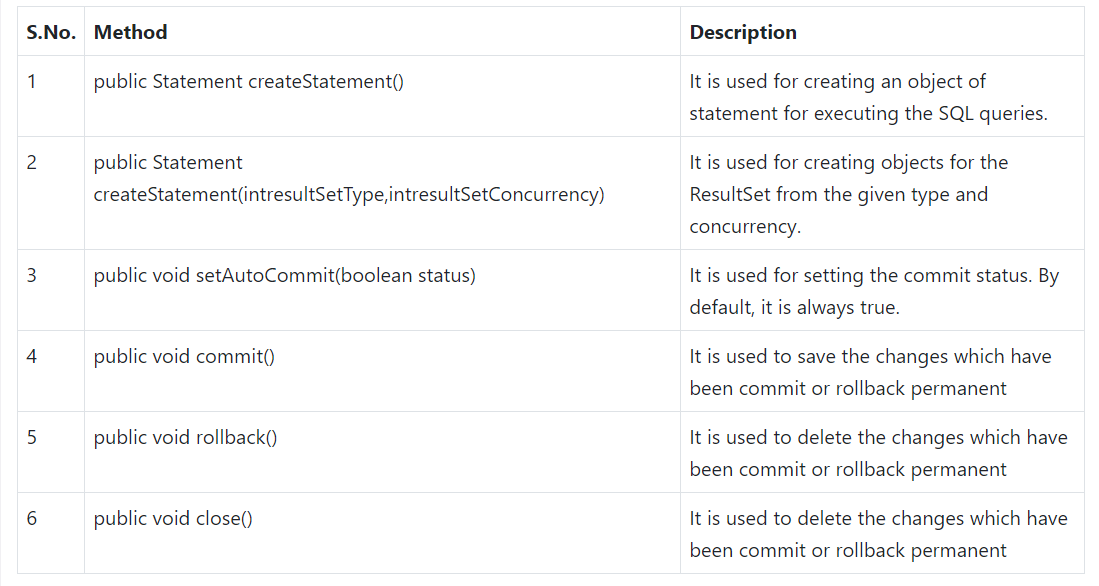
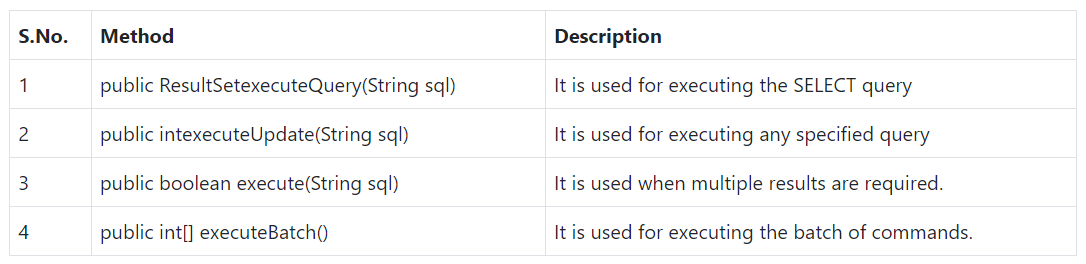
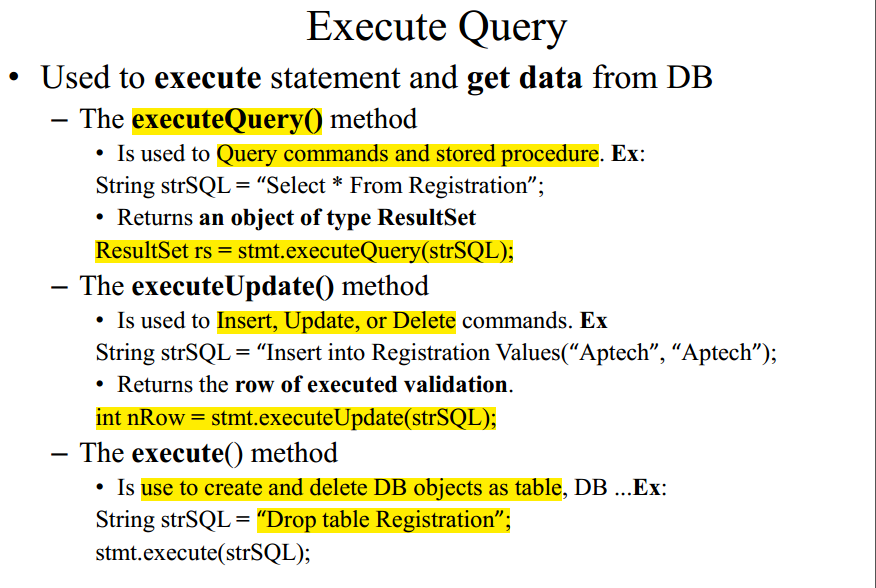
JDBC API
- Java interfaces and classes that support connecting and manipulating with DBs.
- interfaces:
PreparedStatement:
- is a subinterface of Statement.
- is mainly used for parameterized queries.
- A question mark (?) is passed for the values.
- The order of parameters is marked from 1.
- Steps for interpreting:
- First time: 1, 2, 3 like a super statement
- Second time: only 3
CallableStatement
- is used to call a stored procedure.
- ….
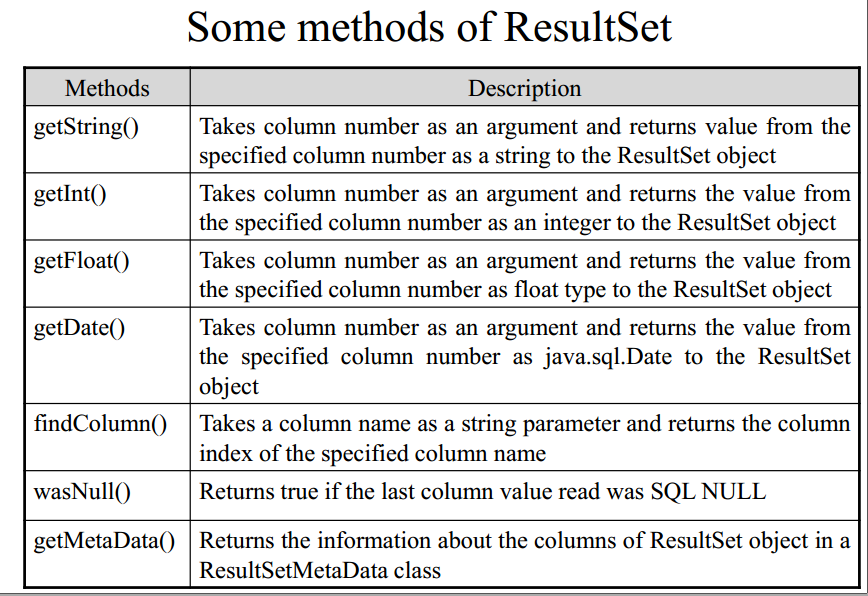
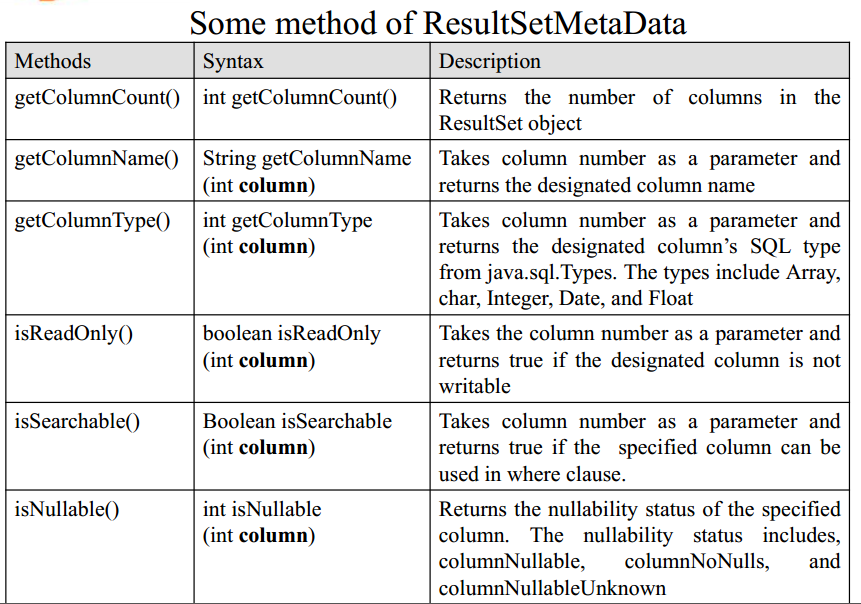
- DatabaseMetadata
- Classes:
- SQLException
💡
💡
💡
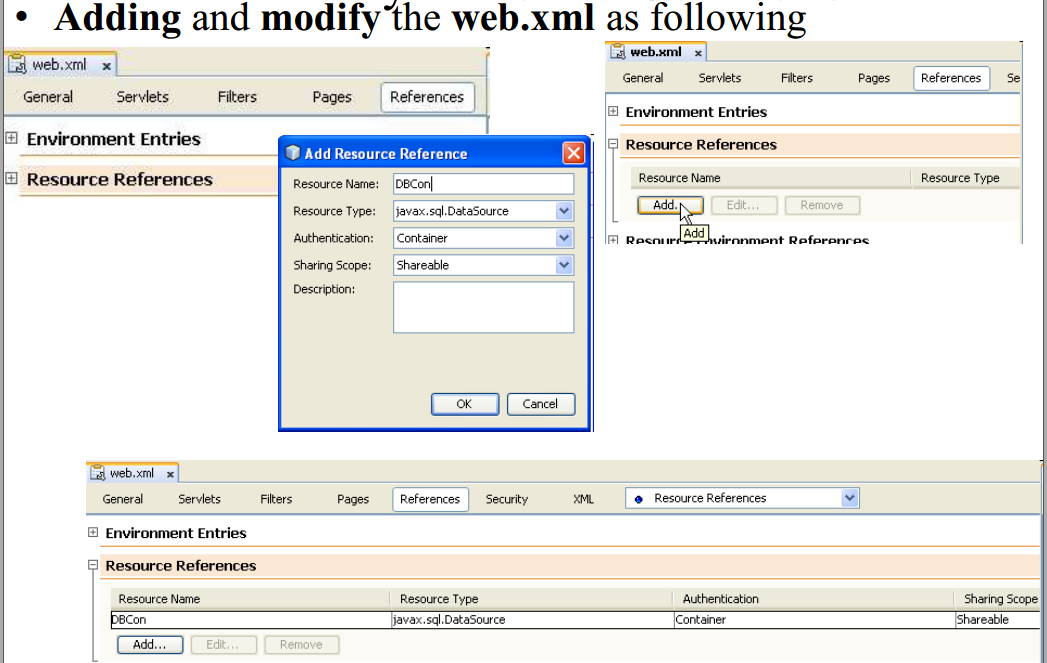
Dynamic DB connection:
Data Source
- is a logical name
- is bind to ip, port, DB, security
References:
.png)